面试题汇总
1. 实现 New 关键字
function New(fn, ...args) {
let obj = {};
obj.__proto__ = fn.prototype;
const ret = fn.apply(this, args);
if (ret instanceof Object) {
return ret;
}
return obj;
}
2. Array.prototype.flat
flat 的作用是根据指定的数组深度摊平数组,可以使用 Infinity(无穷大)展开任意深度的数组
var newArray = arr.flat([depth]);
depth 深度是可选,默认为 1
下面是使用 concat 和 reduce 模拟的 flat
var arr1 = [1, 2, 3, [1, 2, 3, 4, [2, 3, 4]]];
function flatDeep(arr, d = 1) {
return d > 0
? arr.reduce(
(acc, val) =>
acc.concat(Array.isArray(val) ? flatDeep(val, d - 1) : val),
[]
)
: arr.slice();
}
flatDeep(arr1, Infinity);
3. 下面的代码打印什么内容,为什么?
var b = 10;
(function b() {
b = 20;
console.log(b);
})();
- 具名并且自执行函数,函数名只读(类似常量),不可修改
- 非严格模式下给常量命名静默失败,简单来说
b = 20;相当于给函数 b 赋值,于是静默失败 - 严格模式下给常量命名报错 TypeError
4. 二分查找
注意:二分查找是特定在有序数组里才能使用的查找算法
const a = [1, 3, 6, 7, 8, 11, 30, 60, 63, 90];
function binaySearch(array, data) {
const max = array.length - 1; // 9
const mid = Math.floor(max / 2); // 4
if (max < 0) {
return -1;
}
if (array[mid] === data) {
return data;
}
if (array[mid] > data) {
return binaySearch(array.slice(0, mid), data);
} else {
return binaySearch(array.slice(mid + 1, max + 1), data);
}
}
a.forEach((data) => console.log(binaySearch(a, data)));
5. 冒泡排序
Array.prototype.bubbleSort = function () {
let isSorted = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
let haveSort = false;
if (isSorted) {
return;
}
for (let l = 0; l < this.length - 1 - i; l++) {
if (this[l] > this[l + 1]) {
const bigger = this[l];
this[l] = this[l + 1];
this[l + 1] = bigger;
haveSort = true;
}
}
if (!haveSort) {
isSorted = true;
}
}
};
使用haveSort标记一次冒泡中是否有互换,如果没有,表明列表已经是排序完成,结束冒泡
6. 插入排序
插入排序建议结合下图理解
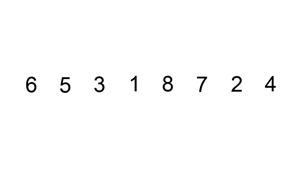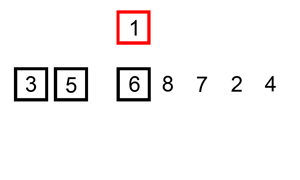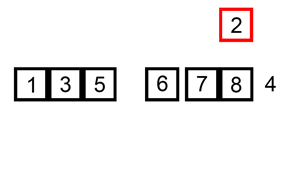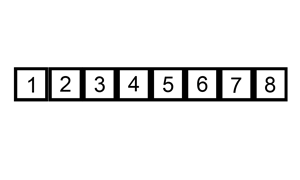
将选取的数插入到已经排序好的数组里
Array.prototype.insertSort = function () {
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
const current = this[i];
let l = i - 1;
while (l >= 0 && current < this[l]) {
this[l + 1] = this[l];
l--;
}
this[l + 1] = current;
}
};
7. 选择排序
每次遍历选择出最小的那个放在最前面
Array.prototype.selectSort = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length - 1; i++) {
let min = i;
for (let l = i + 1; l < this.length; l++) {
if (this[l] < this[min]) {
min = l;
}
}
if (min !== i) {
const bigger = this[i];
this[i] = this[min];
this[min] = bigger;
}
}
};
8. 快速排序
在数组中选择一个作为基准,将小于的放在左边,大于的放在右边,再分别对左边和右边进行同样操作(需要用到递归)
Array.prototype.quickSort = function () {
if (this.length <= 1) {
return this;
}
let mid = this[0],
left = [],
right = [];
for (let i = 1; i < this.length; i++) {
if (this[i] <= mid) {
left.push(this[i]);
} else {
right.push(this[i]);
}
}
return [].concat(left.quickSort()).concat(mid).concat(right.quickSort());
};
9. 实现 call,apply,bind
Function.prototype.CALL = function (context, ...args) {
context.fn = this;
context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
};
Function.prototype.APPLY = function (context, args) {
context.fn = this;
context.fn(...args);
delete context.fn;
};
Function.prototype.BIND = function (context, ...args) {
const self = this;
function RETURNFN(...bindArgs) {
let contextOrThis = context;
if (this instanceof RETURNFN) {
contextOrThis = this;
}
contextOrThis.fn = self;
contextOrThis.fn(...args, ...bindArgs);
delete contextOrThis.fn;
}
RETURNFN.prototype = this.prototype;
return RETURNFN;
};
