虚拟列表
1. 前言
我们先来看个问题:
某天,产品要求我们展示一个大数据列表(几万或者十几万条),但一次性渲染出来会存在性能问题,请问该怎么做?
- 分页
前端分页或者后端分页都可以,这是最常见的处理方式,也是最好的处理方式
那如果产品不想要分页,坚决不要,这时候该怎么办?答案是:
- 虚拟列表
下面的场景,我们来思考下:
一个订单列表容器高 200px,一个订单组件高 50px,也就是说最多能完整显示 4 个订单(部分出现的话是 5 个)
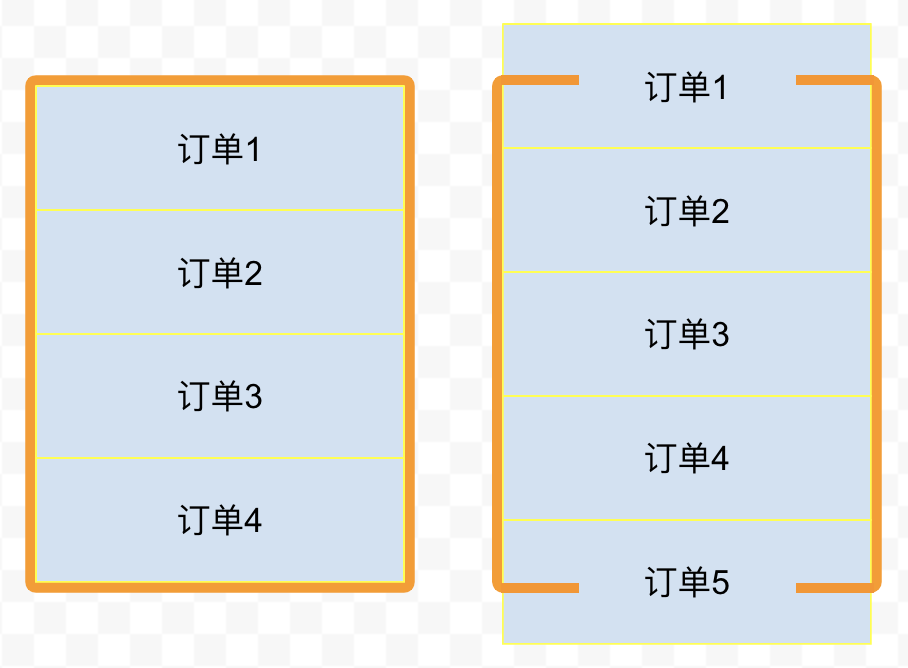
这时后台接口返回 100 个订单,于是我们把 100 个订单都渲染出来

但订单列表容器最多只能显示 5 个订单组件,也就是说订单 6-100 暂时是无用的,只有订单 1-5 是必须渲染的,只需要渲染必要的元素,这就是虚拟列表的核心思想
2. 什么是虚拟列表?
简单来说,就是通过计算,动态展示列表的一部分,达到节约资源的效果
通过scrollTop可以知道一个元素的内容垂直滚动的像素大小,计算出当前位置对应原列表元素的 index,从而渲染需要的列表部分
虚拟列表滚动过程:
<div style="display: flex; align-items: center; text-align: center;">
<div>
<img src={require("./assets/screenshots/23.png").default} width="150" />
<p>(1)初始状态</p>
</div>
<span> => </span>
<div>
<img src={require("./assets/screenshots/24.png").default} width="150" />
<p>(2)滑动一段距离</p>
</div>
<span> => </span>
<div>
<img src={require("./assets/screenshots/25.png").default} width="150" />
<p>(3)重新渲染后</p>
</div>
</div>
3. 固定高度实现
在滚动后,我们需要计算 top 的值

top为4个订单的高度
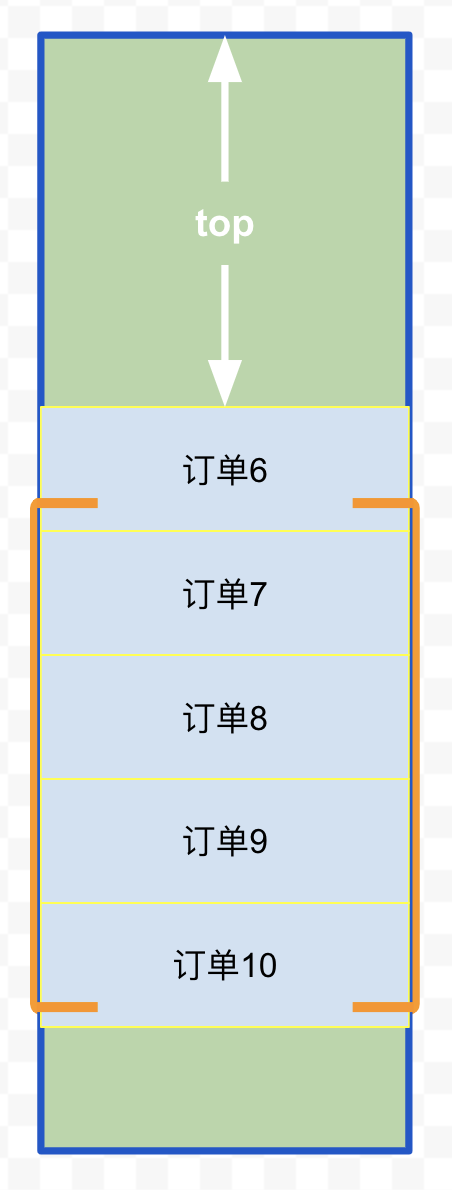
top为5个订单的高度
下面代码为了直接体现虚拟列表的实现,没有进行 api 抽象,详细请看:github
import React, { Component } from "react";
class VirtualList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.list = new Array(100000).fill(null).map((_, index) => {
return index + 1;
});
this.height = 600; //容器高度
this.itemHeight = 60; //单个子元素高度
this.state = { visibleData: [], startOffset: 0, offsetHeight: 0 }; //初始化数据
this.totalHeight = this.list.length * this.itemHeight; //原列表总高度
this.visibleCount = Math.ceil(this.height / this.itemHeight); //容器可以显示的个数(向上取整)
this.startIndex = 0; //开始的index
this.endIndex = this.startIndex + this.visibleCount; //结束的index
}
componentDidMount() {
this.updateVisibleData(); //更新列表
}
updateVisibleData = () => {
const visibleData = this.list.slice(this.startIndex, this.endIndex);
const startOffset = this.startIndex * this.itemHeight;
const offsetHeight = visibleData.length * this.itemHeight;
this.setState({
visibleData,
startOffset,
offsetHeight,
});
};
handleScroll = (e) => {
const scrollTop = this.node.scrollTop;
const index = scrollTop / this.itemHeight;
this.startIndex = Math.floor(index);
this.endIndex =
this.startIndex + this.visibleCount + (index % 1 > 0 ? 1 : 0); //因为startIndex向下取整,所以endIndex需要根据情况适当+1
this.updateVisibleData();
};
renderListItem = (item) => {
return (
<div
key={item}
style={{
height: this.itemHeight,
boxSizing: "border-box",
borderBottom: "1px solid black",
}}
>
{item}
</div>
);
};
render() {
const { visibleData, startOffset, offsetHeight } = this.state;
return (
<div
style={{
position: "relative",
overflowY: "auto",
height: this.height,
border: "1px solid black",
}}
ref={(node) => (this.node = node)}
onScroll={this.handleScroll}
>
<div style={{ height: this.totalHeight }}>
<div
style={{
position: "absolute",
left: 0,
right: 0,
top: startOffset,
height: offsetHeight,
}}
>
{visibleData.map(this.renderListItem)}
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
}
}
export default VirtualList;
除了设置height来撑开滚动容器的高度,还可以使用padding和margin,但需要额外计算 bottom 的距离

4. 测试
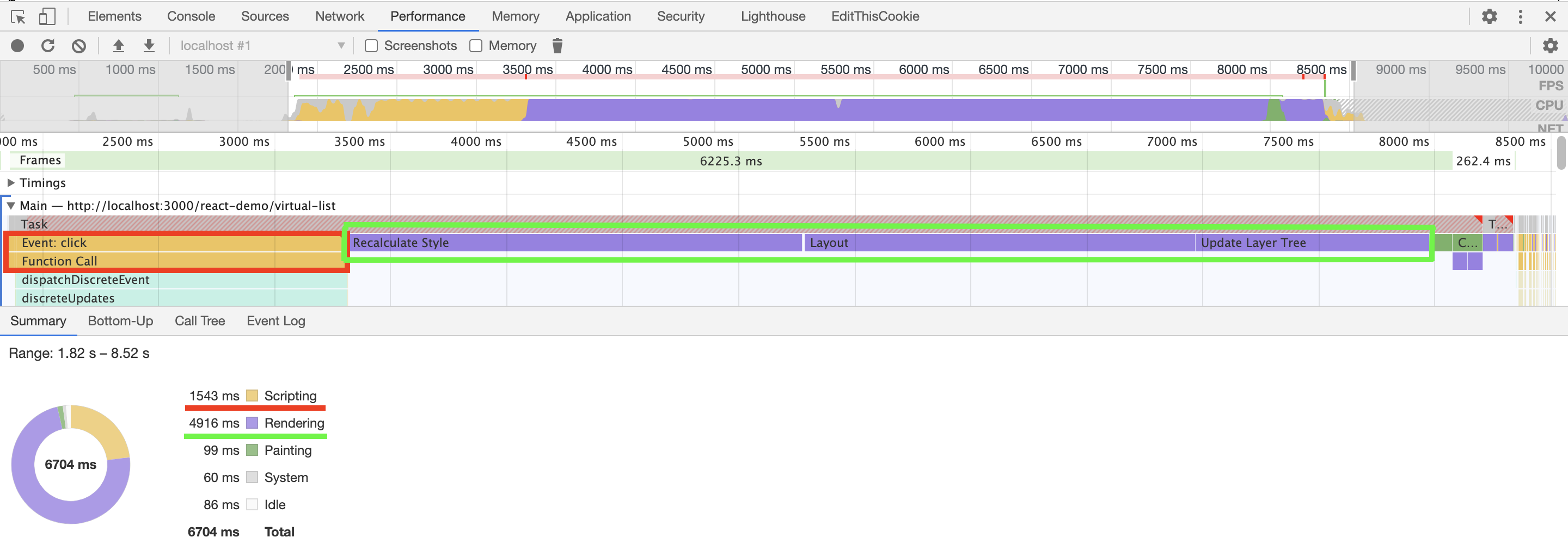
下面是 react 创建长度为 100000 的列表需要的时间,其中渲染和 js 脚本占了大部分时间,分别是 4.9s 和 1.5s,渲染久很容易理解,毕竟需要处理 100000 个 dom 元素,脚本久主要是因为 react 里虚拟 dom 处理的原因
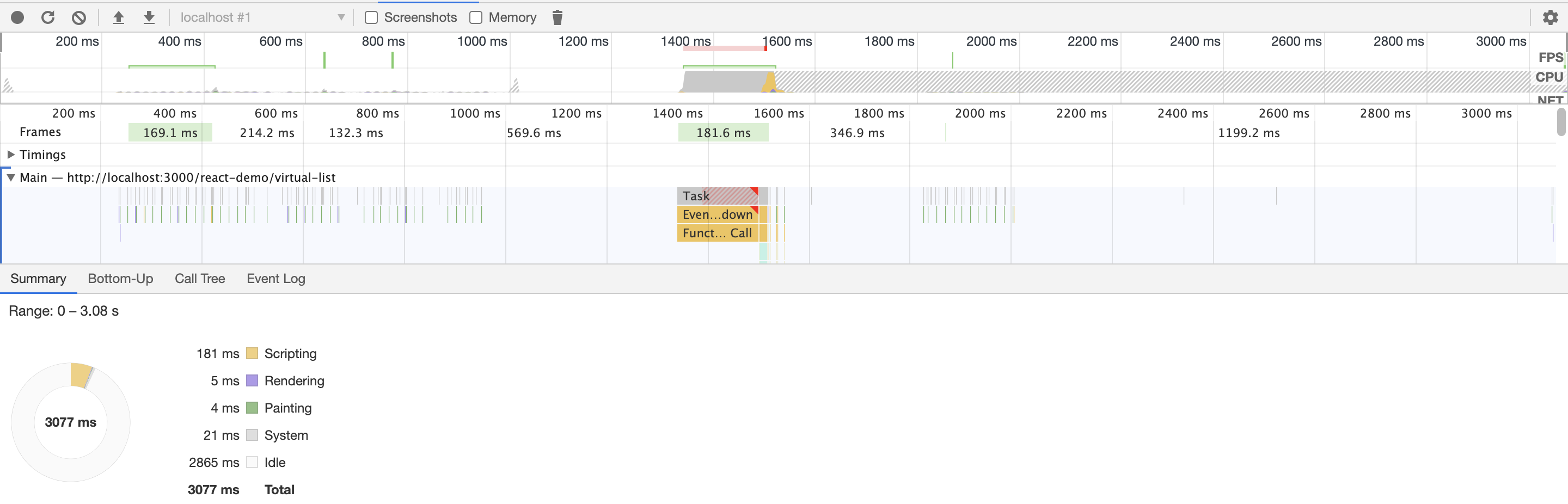
再下面是 react 创建长度为 100000 的虚拟列表需要的时间,可以看到 0.5s 都不到就渲染好了
5. 白屏?
有好处就有坏处,虚拟列表在快速滑动时,onScroll事件响应的速度如果未能跟上滑动的速度,就会导致向下滑动话新的页面没能及时渲染出来,这就是白屏问题
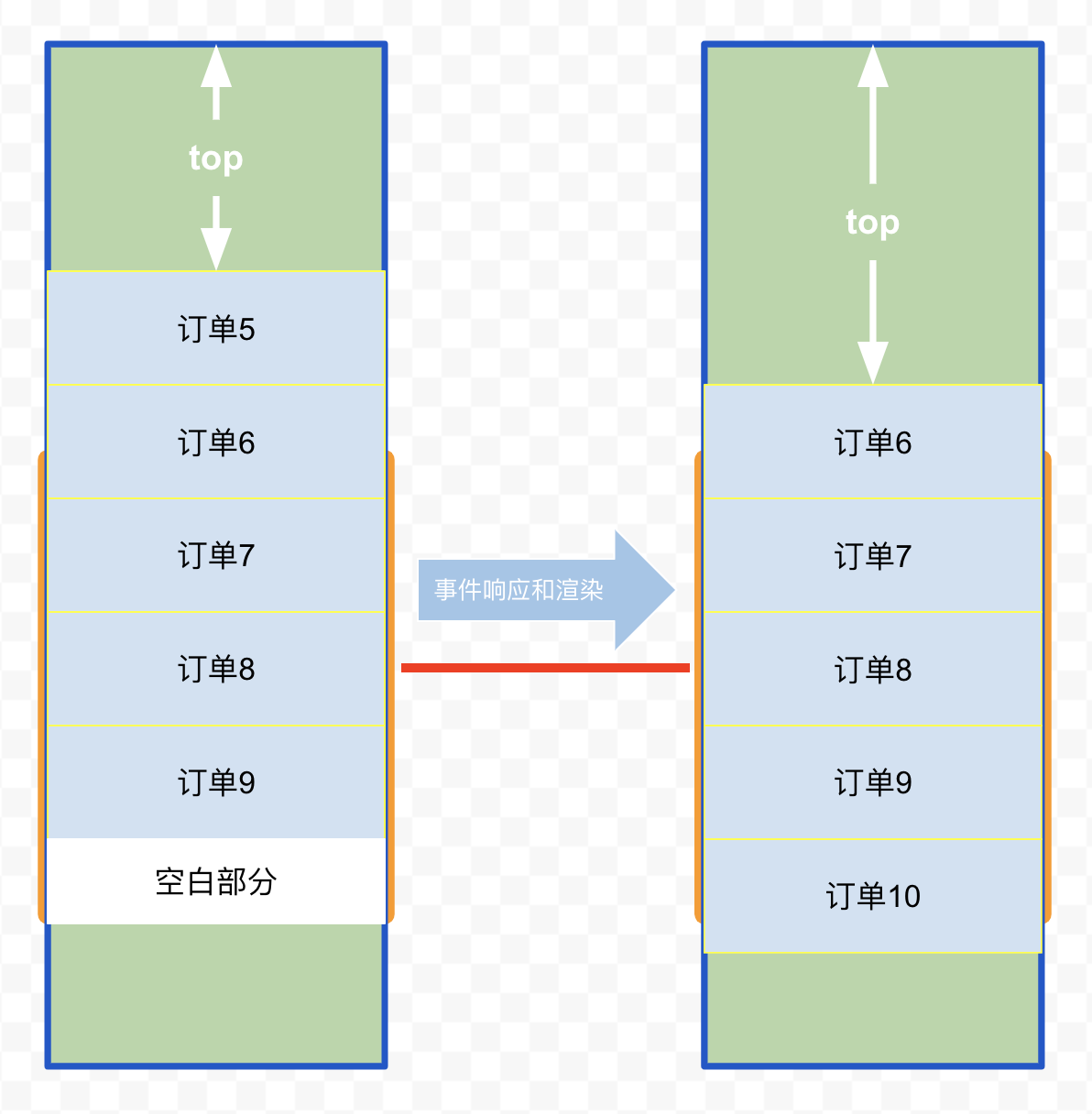
可以尝试缓存的方式,在首尾额外渲染一部分的元素,有一定缓存距离,这样不那么容易出现白屏问题,但事实上,滑动速度要是快过缓存距离还是会有白屏现象,尤其是拖动滚动条,所以说并不能完全解决问题
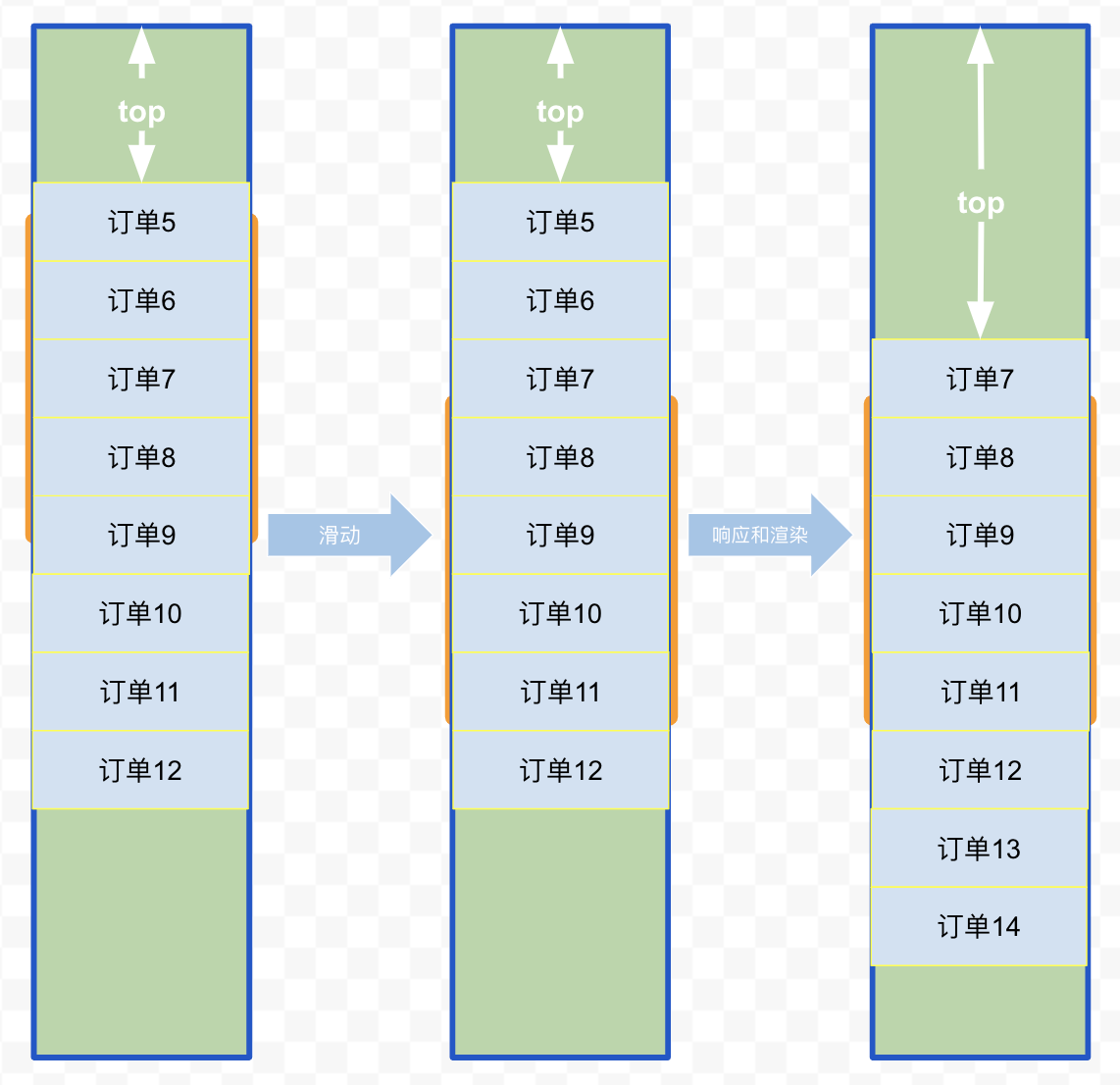
上面图示里,订单列表尾部多渲染了 3 个订单作为缓存,只要一次滑动的距离不超过 3 个订单高度,即使事件响应和渲染速度较慢,也不会出现白屏问题(向上滑动同理,只要首部增加缓存即可)
6. 缓存
增加缓存只需要修改startIndex和endIndex的逻辑即可
import React, { Component } from "react";
class VirtualList extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.list = new Array(100000).fill(null).map((_, index) => {
return index + 1;
});
this.cache = 5; //首尾缓存数量
... //省略
this.endIndex = this.startIndex + this.visibleCount + this.cache; //结束的index
}
...
handleScroll = e => {
const scrollTop = this.node.scrollTop;
const index = scrollTop / this.itemHeight;
const startIndex = Math.floor(index);
const offsetIndex = index % 1 > 0 ? 1 : 0;
if (startIndex >= this.cache) {
this.startIndex = startIndex - this.cache;
} else {
this.startIndex = 0;
}
if (
startIndex >=
this.list.length - (this.visibleCount + this.cache + offsetIndex)
) {
this.endIndex = this.list.length;
} else {
this.endIndex = startIndex + this.visibleCount + this.cache + offsetIndex;
}
this.updateVisibleData();
};
...
增加cache参数,修改handleScroll函数
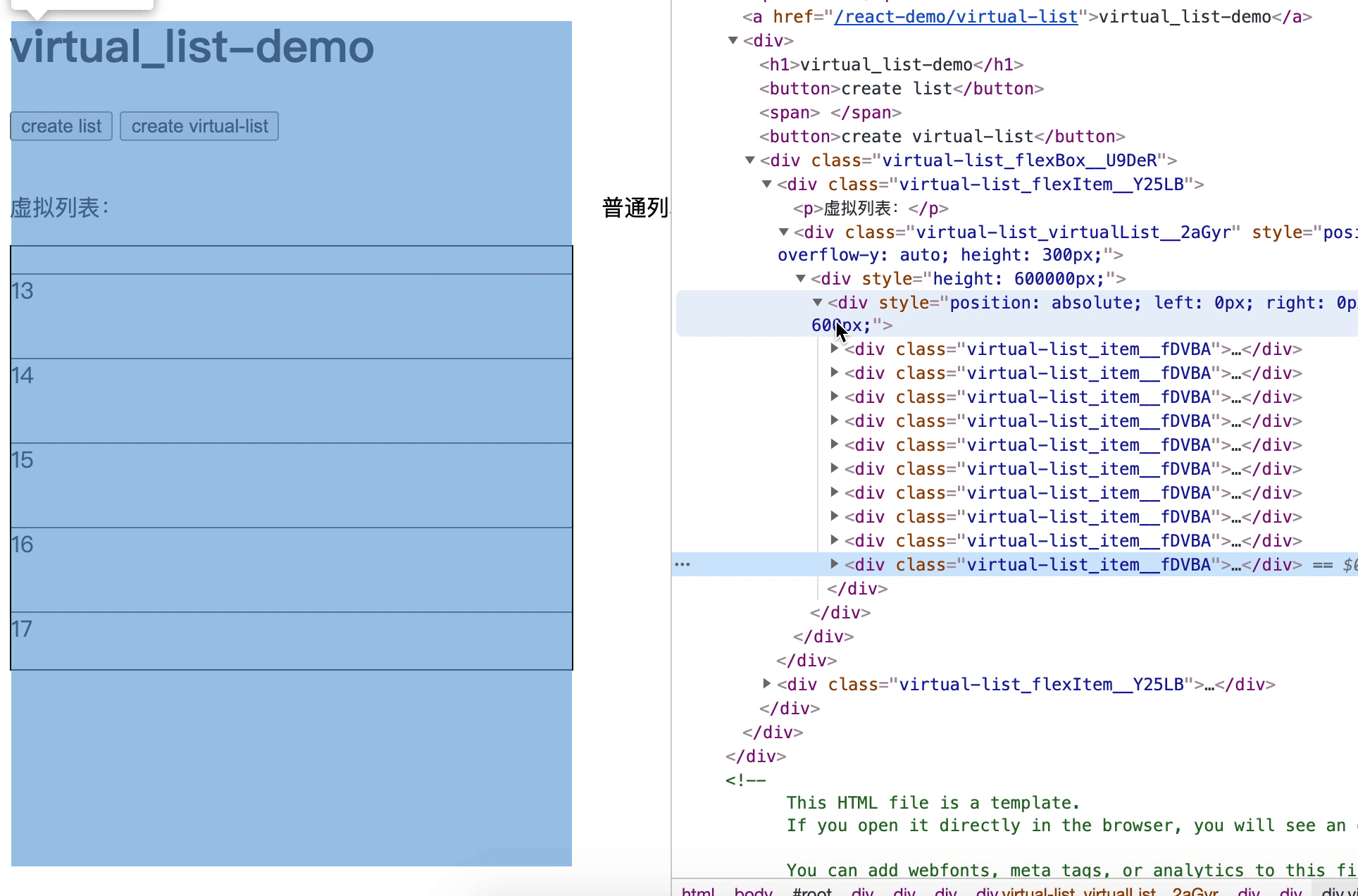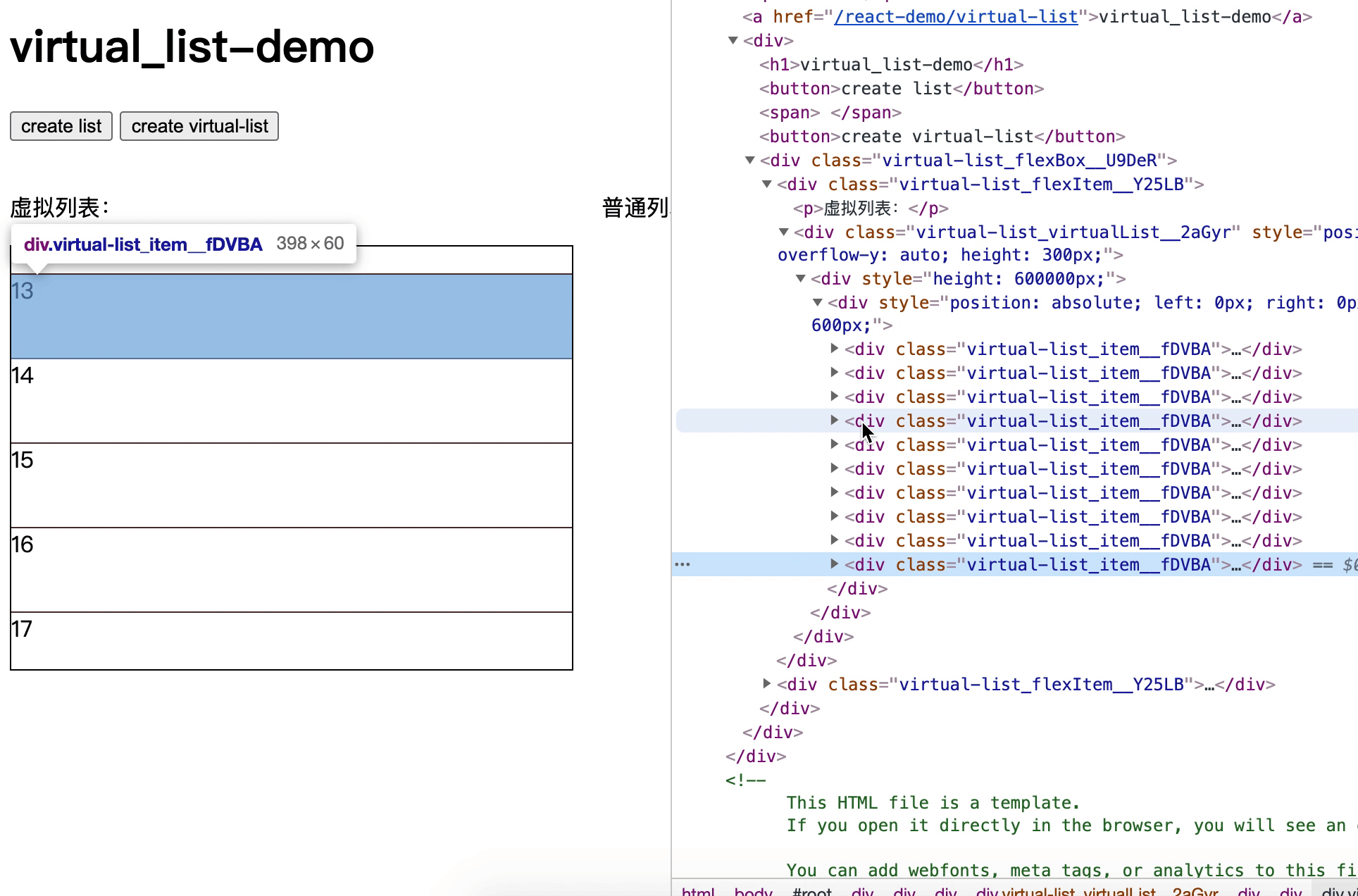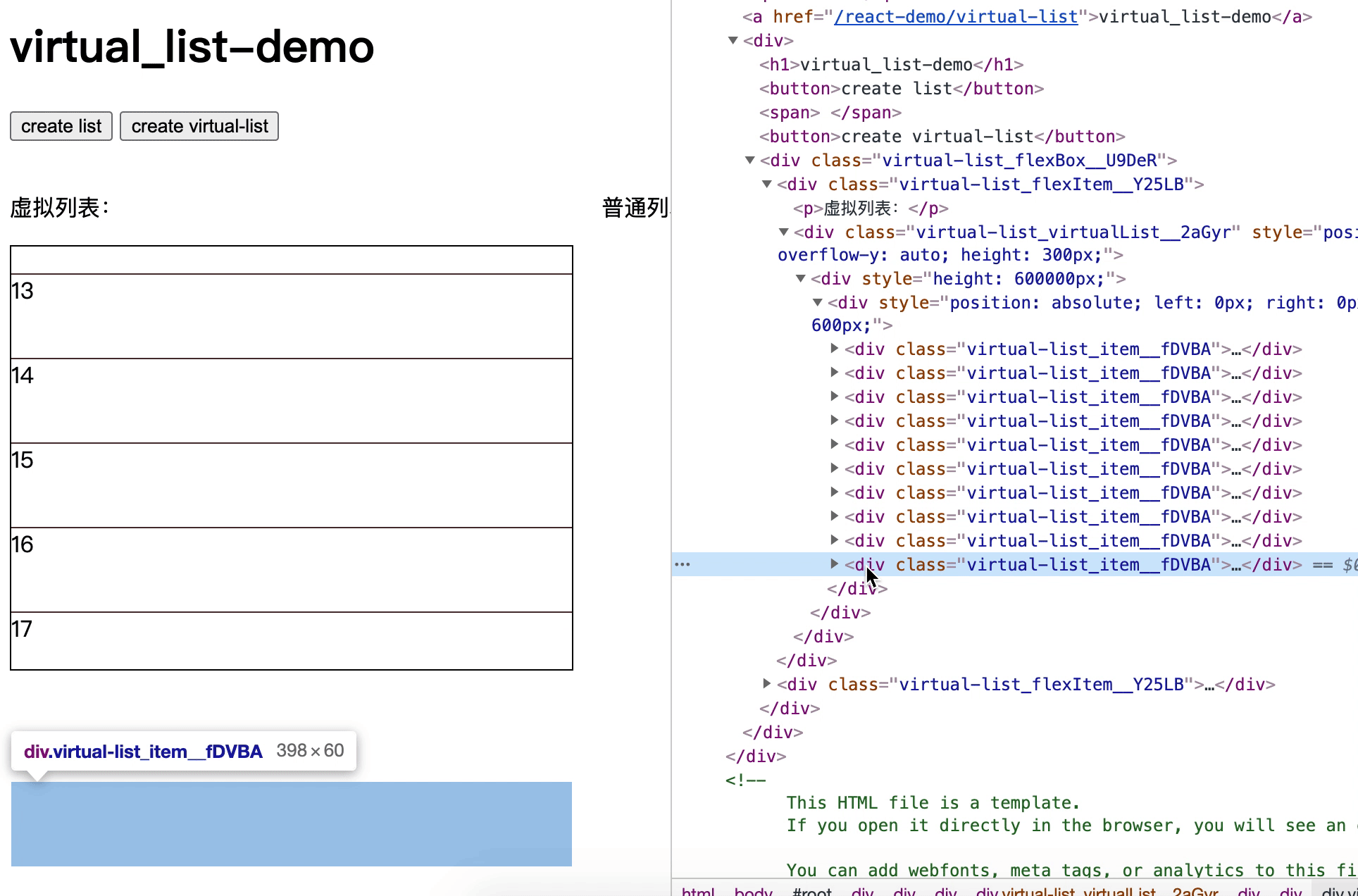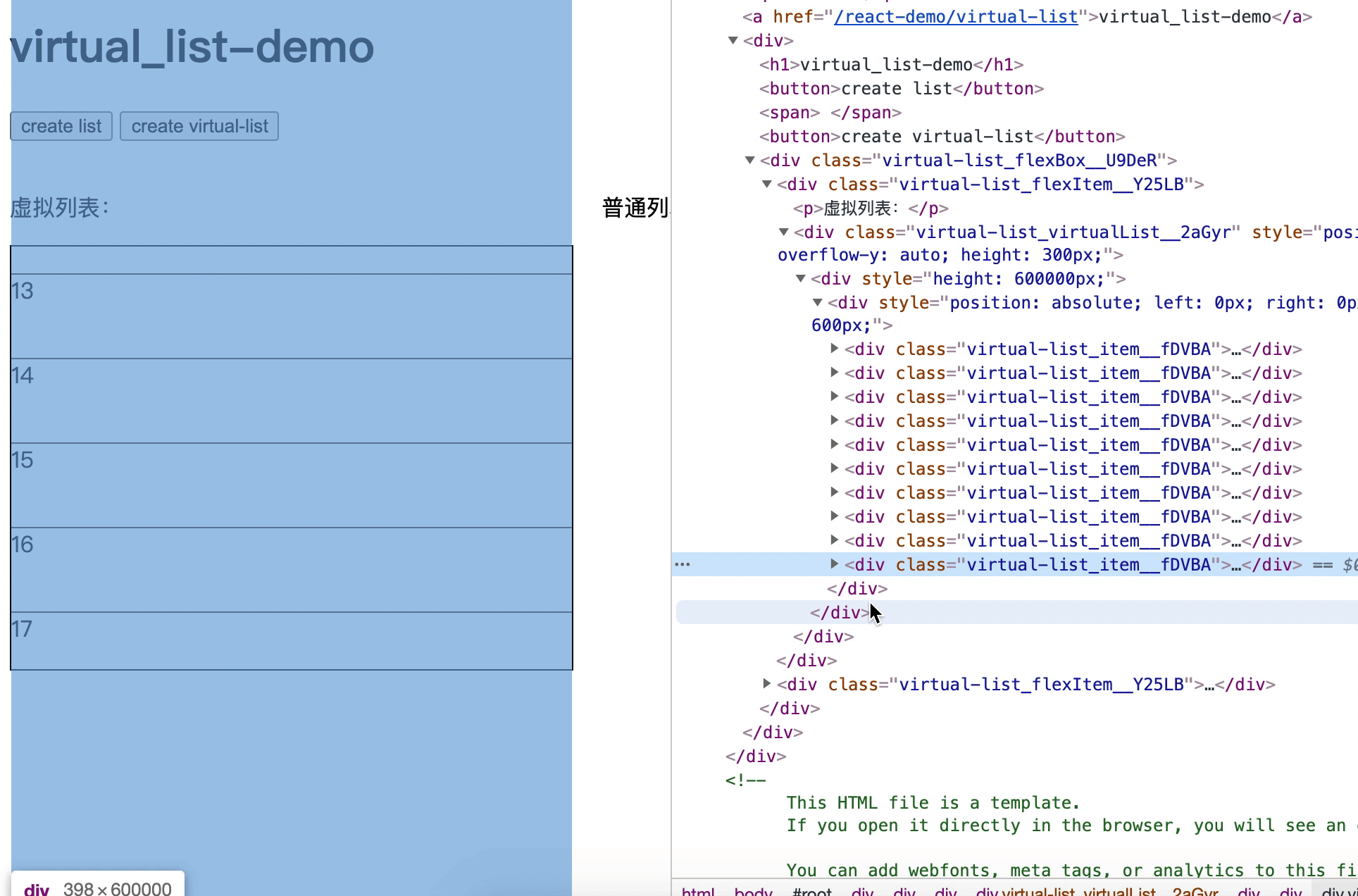
7. 动态高度实现
上面的场景和实现都是以列表子元素固定高度来实现,那如果高度不固定该怎么办?
未完待续...
